India’s transition to clean energy is gaining momentum, and solar power is at the heart of this shift. With rising electricity costs, frequent outages in some regions, and government-backed incentives, more homeowners and businesses are considering solar panel systems. But one critical question remains: should you choose an on-grid or off-grid solar system?
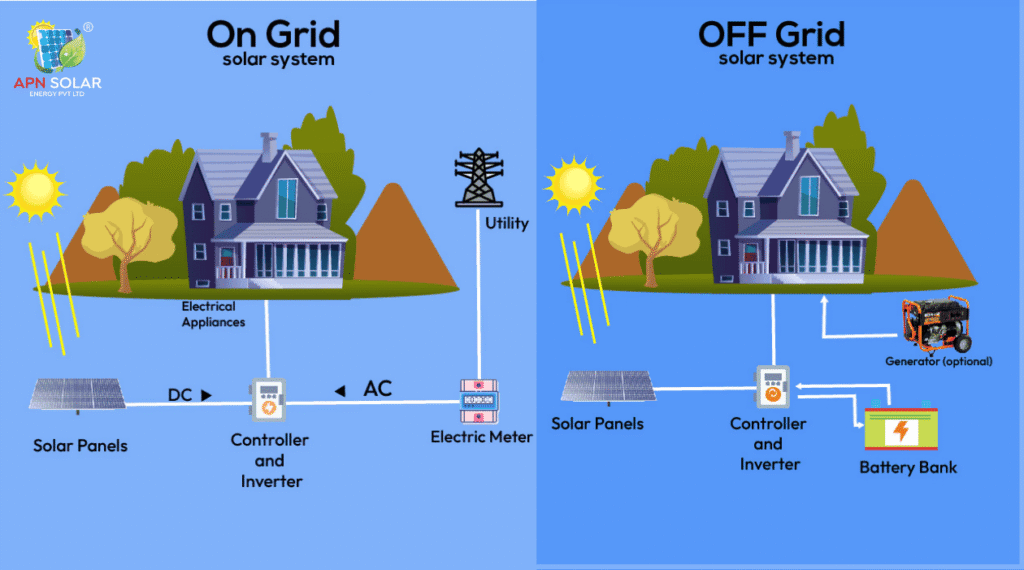
An on-grid solar system is connected to the main electricity grid and allows users to export excess power via net metering. In contrast, an off-grid system operates independently using batteries for backup, making it ideal for areas with unreliable or no grid access.
In this guide, we’ll compare the two systems based on cost, efficiency, backup capability, and suitability for various regions in India. Whether you’re in a metro city or a remote village, this article will help you decide which solar setup is better for your needs and environment.
What Is an On-Grid Solar System?
An on-grid solar system, also known as a grid-tied or grid-connected solar system, is a type of solar power setup that is directly linked to the electricity grid managed by your local DISCOM (Distribution Company). This system is designed to generate electricity from the sun during the day and supply it to your home or business. Any surplus electricity that isn’t used immediately is automatically sent back to the main grid through a process known as net metering.
In an on-grid system, there are no batteries involved. Instead of storing unused solar energy, the system feeds it into the public grid, allowing users to earn credits that are adjusted in their monthly electricity bills. This makes it a cost-effective and low-maintenance solution for energy-conscious homeowners and businesses in areas with stable power supply.
How It Works with DISCOM and Net Metering
When you install an on-grid solar system, it gets integrated with a bidirectional (net) meter, which records both the electricity you consume from the grid and the excess electricity your system exports. DISCOMs then adjust your bill based on the net usage if you export more than you import, your bill can be significantly reduced or even zero.
Each Indian state has its own net metering policy. For example, Delhi, Maharashtra, and Gujarat have robust frameworks supporting residential solar adoption through grid-tied systems.
Ideal Scenario: Urban Indian Homes
Example: A family in Pune installs a 5kW on-grid solar system. Their monthly power bill drops from ₹4,000 to just ₹500, thanks to consistent sunlight and Maharashtra’s favorable net metering regulations. The system paid for itself in just 4.5 years, with an expected lifespan of 25 years.
Pros and Cons of On-Grid Solar System
| Advantages | Limitations |
| Lower upfront cost (no battery required) | No electricity during grid outages |
| Eligible for net metering credits | Fully dependent on grid availability |
| Simple to maintain | Requires DISCOM approvals and inspections |
| Ideal for urban homes with reliable power | Not suitable for rural/off-grid areas |
What Is an Off-Grid Solar System?
An off-grid solar system, also known as a standalone solar system, is a self-sustaining energy setup that operates independently of the main electricity grid. Unlike on-grid systems, off-grid solar systems store excess energy in batteries, making them a reliable source of power in locations where grid connectivity is poor, unreliable, or entirely unavailable.
The system typically includes solar panels, a charge controller, batteries for energy storage, and an inverter to convert DC electricity into AC. The batteries ensure that energy generated during the day can be used at night or during cloudy weather providing round-the-clock power without relying on the grid.
This system is especially beneficial in remote areas, rural villages, mountainous regions, and farms in India, where power cuts are frequent or infrastructure is limited.
Ideal Scenario: Rural and Off-Grid Areas
Example: A farmer in Leh, Ladakh installs a 3kW off-grid solar system with battery backup to run irrigation pumps and household appliances. Despite zero grid access, the system provides uninterrupted electricity even during harsh winters.
Pros and Cons of Off-Grid Solar System
| Advantages | Limitations |
| Complete energy independence | Higher initial cost due to batteries |
| Ideal for rural/off-grid areas | Limited energy storage based on battery capacity |
| Reliable power during outages | Regular battery maintenance required |
| No reliance on government infrastructure | No net metering or export benefits |
Differences Between On-Grid and Off-Grid Solar Systems
When choosing between an on-grid and an off-grid solar system, it’s essential to understand how they differ in terms of cost, functionality, energy independence, and real-world application. Each system serves a unique purpose depending on your location, electricity needs, and grid availability.
Below is a side-by-side comparison that outlines the core differences between these two solar power setups:
Comparison Table: On-Grid vs Off-Grid Solar Systems
| Parameter | On-Grid Solar System | Off-Grid Solar System |
| Grid Connection | Connected to the main electricity grid | Operates independently without grid |
| Battery Requirement | Not required | Mandatory for energy storage |
| Initial Cost | Lower (no battery needed) | Higher (includes battery system) |
| Electricity Backup | No power during outages | Provides full backup via batteries |
| Net Metering Eligibility | Yes, excess power exported for credits | No, no connection to the grid |
| Maintenance | Minimal, mainly inverter and panels | Requires regular battery maintenance |
| Best Suited For | Urban homes, offices, factories with reliable power | Rural areas, farms, off-grid homes |
| Government Subsidies | Available under grid-tied solar policies | May be limited or location-specific |
| Energy Independence | Partial (depends on grid) | Full independence from grid supply |
| Lifespan of System | 25+ years | 20–25 years (batteries need replacement earlier) |
Which Solar System Is Better in Indian?
The decision between an on-grid and off-grid solar system in India depends heavily on location-specific factors, such as power reliability, local DISCOM policies, climate conditions, and infrastructure development.
State-wise Applicability: Where Off-Grid Works Best
In remote or under-electrified regions, off-grid systems are often the only viable solution. States and regions where off-grid solar is most suitable include:
- North-Eastern States: Assam, Meghalaya, and Nagaland face limited grid penetration and frequent outages.
- Himalayan Region: Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and Ladakh experience harsh winters, grid failures, and remote settlements making off-grid essential.
- Desert & Tribal Regions: Rajasthan (interior desert zones), Odisha (tribal areas), and parts of Chhattisgarh benefit from battery-based solar systems due to inconsistent electricity supply.
In these locations, off-grid systems can power homes, schools, clinics, and farms helping bridge the rural-urban energy divide.
Electricity Reliability & Infrastructure
India’s urban areas have made significant progress in grid reliability. Cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Pune, and Bengaluru enjoy consistent power, making on-grid systems the more economical and scalable choice especially with net metering incentives and rising rooftop solar programs under state DISCOMs.
Policy & Government Support
- On-grid solar is supported by net metering, which allows users to export excess power and earn credits. Most states, including Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, and Maharashtra, have favorable rooftop solar policies.
- Off-grid systems receive support under schemes like PM-KUSUM (for farmers) and Saubhagya Yojana (rural electrification).
Visit MNRE (Ministry of New and Renewable Energy) for official policy documents and subsidy details.
Expert Perspective
“In semi-urban regions where grid stability is moderate, we often recommend a hybrid solar system combining the flexibility of battery backup with the cost-effectiveness of net metering.”
— Dr. Rajiv Sharma, Solar Consultant, MNRE-Accredited
Cost Comparison: On-Grid vs Off-Grid Solar Panels in India
When investing in solar energy, understanding the total cost of ownership is critical. While both on-grid and off-grid solar systems help reduce electricity bills, their initial investment, component costs, and return on investment (ROI) differ significantly.
1. Installation Cost Breakdown
| Component | On-Grid (₹/kW) | Off-Grid (₹/kW) |
| Solar Panels | ₹25,000 – ₹30,000 | ₹25,000 – ₹30,000 |
| Inverter | ₹10,000 – ₹15,000 | ₹15,000 – ₹25,000 |
| Batteries | Not required | ₹25,000 – ₹40,000 |
| Wiring & Mounting | ₹5,000 – ₹8,000 | ₹5,000 – ₹8,000 |
| Total Avg Cost | ₹45,000 – ₹55,000 per kW | ₹70,000 – ₹1,00,000 per kW |
Off-grid systems are costlier due to the inclusion of deep-cycle batteries for storage. Battery type (lead-acid vs lithium-ion) can further affect costs.
2. Battery Cost & Lifespan
Off-grid systems require battery replacement every 5–7 years, adding to the long-term maintenance expense. Lithium-ion batteries cost more upfront but last longer and require less maintenance.
3. Maintenance Cost
- On-Grid: Minimal – mostly inverter and panel cleaning.
- Off-Grid: Higher – due to battery monitoring, fluid checks, and capacity degradation.
4. Return on Investment (ROI)
| System | ROI Period | Best Fit |
| On-Grid | 4–6 years (with net metering) | Urban homeowners, offices |
| Off-Grid | 6–10 years (longer due to batteries) | Rural areas, remote applications |
Follow this step-by-step solar panel installation guide to get your on-grid or off-grid solar system up and running.
Hybrid Solar Systems: A Middle Ground?
A hybrid solar system combines the best of both worlds on-grid and off-grid solar technologies. It connects to the main electricity grid (like an on-grid system) while also including battery storage (like an off-grid system), enabling it to function both with and without grid power.
What Is a Hybrid Solar System?
A hybrid system consists of solar panels, a hybrid inverter, batteries, and grid connectivity. During the day, solar energy powers your appliances and charges the batteries. If excess power is generated, it’s sent to the grid via net metering. In case of a power outage or nighttime usage, the system draws energy from the batteries ensuring uninterrupted power supply.
When Should You Consider a Hybrid Solar System?
- You live in semi-urban areas with frequent but short power cuts
- You want the reliability of a backup system without fully going off-grid
- You wish to optimize savings through net metering but also want power security
Example: A homeowner in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, chooses a 5kW hybrid system to maintain backup during outages while earning credits from surplus production.
Before deciding, it’s important to choose the right components for your setup. Not sure which panel fits your system type? Read about the different types of solar panels used in India. You can also understand how monocrystalline vs polycrystalline panels impact efficiency in both on-grid and off-grid setups.
Cost vs Flexibility Trade-Off
While hybrid systems cost more than traditional on-grid setups (due to battery inclusion), they provide maximum flexibility, energy independence, and security against blackouts.
| Feature | Hybrid System |
|---|---|
| Upfront Cost | ₹75,000–₹1,10,000 per kW |
| Battery Backup | Yes |
| Net Metering | Eligible |
| Best For | Homes with unstable grid power |
Expert Recommendation: How to Choose Between On-Grid and Off-Grid
By Dr. S.P. Gon Chaudhuri – Chairman, NBIRT (National Biodiversity Institute of Renewable Technology), Former Director of WBREDA, Advisor to MNRE
As someone who has spent over three decades in the field of solar energy and rural electrification in India, I can say confidently that choosing between an on-grid and off-grid solar system is not a one-size-fits-all decision. It requires evaluating your power reliability, geographic location, usage profile, and long-term energy goals.
How to Decide What’s Best for You
If you’re unsure where to begin, here’s a practical decision matrix I’ve used in countless residential and community solar consultations:
| Question | If Yes → Recommended System |
| Do you have reliable power supply from the DISCOM? | On-Grid |
| Do you face frequent power cuts or load-shedding? | Off-Grid or Hybrid |
| Do you want to monetize surplus electricity via net metering? | On-Grid |
| Are you located in a remote or mountainous area with no grid access? | Off-Grid |
| Do you need energy independence + backup during outages? | Hybrid |
| Is your primary goal cost-saving without investing in batteries? | On-Grid |
Use-Case Comparisons from Real Installations
Urban Apartment in Pune (On-Grid):
One of our residential clients in a 3BHK flat installed a 3kW on-grid system. Thanks to the Maharashtra net metering policy, their power bill dropped from ₹2,700/month to less than ₹500, recovering their investment in under 5 years.
Remote Farmhouse in Jharkhand (Off-Grid):
In a tribal belt outside Ranchi, a small dairy farm runs entirely on a 5kW off-grid system with lithium-ion batteries, operating freezers, lights, and irrigation motors a complete off-grid solution with zero grid dependence.
If you live in a metro or tier-1 city, on-grid systems offer maximum economic return through net metering and government subsidies. However, if you face frequent blackouts or live in semi-rural zones, a hybrid system gives you the best of both worlds: bill savings + backup.
For completely remote regions, especially in the Himalayan belt, Northeastern states, or tribal interiors, only off-grid systems can provide sustainable, round-the-clock power.
Simplifying Solar Adoption in India: Why Trusted Providers Matter
Deciding between an on-grid or off-grid solar system is just one part of the journey. Ensuring that your system is properly installed, subsidy-compliant, and technically optimized requires working with a solar company that’s both reliable and government-approved.
One such trusted provider is APN Solar best solar company in India and a proud participant in the PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana. Registered on the National Rooftop Solar Portal, APN Solar helps customers across India access government subsidies with ease and confidence.
Backed by a team of solar engineers, project managers, and clean energy professionals, APN Solar offers:
- Expert installation of on-grid, off-grid, and hybrid solar systems
- End-to-end support for MNRE subsidy registration and net metering
- Use of BIS and TUV-Rheinland certified components
- Commitment to quality, safety, and sustainability
As an ISO 9001:2015, ISO 45001:2018, and ISO 14001:2015 certified OEM manufacturer, APN Solar stands out for its dedication to delivering affordable, high-performance solar solutions across both urban and rural India.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between on-grid and off-grid solar systems?
On-grid solar systems are connected to the main electricity grid and rely on it for backup. Off-grid systems, on the other hand, work independently using batteries to store power for use during non-sunny hours or power outages. On-grid is ideal for cities, while off-grid suits remote areas.
2. What is an off-grid solar system?
An off-grid solar system is a standalone energy setup that operates without any connection to the electricity grid. It uses solar panels and battery storage to power appliances 24/7, making it suitable for remote locations or areas with unreliable electricity supply.
3. Which is better: on-grid or off-grid solar system?
The best solar system depends on your location and energy needs. Use on-grid if you have a stable grid connection and want to reduce bills via net metering. Choose off-grid if you need complete energy independence or live in a remote area without grid access.
4. What is the difference between off-grid and hybrid solar systems?
Off-grid systems operate completely independently with battery storage, while hybrid systems combine both grid connectivity and battery backup. Hybrid solar offers the flexibility of grid power when needed and battery backup during outages, making it ideal for semi-urban areas.
5. What is the disadvantage of an on-grid solar system?
The main disadvantage of an on-grid system is that it does not work during power cuts. Without battery backup, you lose access to solar power when the grid is down. This can be a challenge in areas with frequent blackouts.
6. How do I set up an off-grid solar power system at home?
To set up an off-grid solar system, you’ll need solar panels, a charge controller, batteries, and an inverter. Start with a load assessment, choose a certified installer like APN Solar, and apply for applicable state or central government schemes if available.
7. What is the cost of a 3kW solar panel system in India?
As of 2026, a 3kW on-grid solar system costs ₹1.5–₹1.8 lakh, while an off-grid system with battery costs ₹2.2–₹2.7 lakh. To decide, compare solar costs and government subsidies for each system, as prices vary by quality, location, and services.



Ihave installed solar system of 5kw.last month i produce 496 solar units but net meter shows only 320 units.
Can it is possible to generation of electric energy while electricity cut in On grid solar system ?
I want a 5kw hybrid solar plant at Kansal Punjab. Give the quote forbest technology with subsidy option.
For any inquiries, please email us at sales@apnsolar.com or call our toll-free number: 1800 202 6150.
Good.Neatly explained to understand to take a decision.
Good to know about on grid & off grid solar system.